“If You Fail to Plan, You Are Planning to Fail” — Benjamin Franklin.
Project planning is immensely underrated. Everyone has a story of how they could have planned better to avoid a disaster, even if they didn’t look back and realize it.
Project planning ensures project success and timely delivery, a crucially important function in any technical organization. Striving toward a perfect plan will help increase the probability of customer satisfaction and their trust in the organization for future investments. It’s the most crucial step in the reduction of risk and project failures. After all, no one gets points for a brilliant idea if the execution ultimately fails.
The following article covers the basics of project planning, its fundamentals, why it’s so important for organizations, some popular tools used for project planning, and basic steps. We’ll also look at some opportunities to learn about these tools in more depth.
What is Project Planning?
A project consists of five different phases: initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and controlling, and closure. Planning is the second phase of the project life cycle, where a plan after the initiation phase is made so the process of execution may begin. The project plan serves as a roadmap for the entire process of project management.
Project planning ensures project success and timely delivery, a crucially important function in any technical organization. Striving toward a perfect plan will help increase the probability of customer satisfaction and their trust in the organization for future investments. It’s the most crucial step in the reduction of risk and project failures. After all, no one gets points for a brilliant idea if the execution ultimately fails.
The following article covers the basics of project planning, its fundamentals, why it’s so important for organizations, some popular tools used for project planning, and basic steps. We’ll also look at some opportunities to learn about these tools in more depth.
What is Project Planning?
A project consists of five different phases: initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and controlling, and closure. Planning is the second phase of the project life cycle, where a plan after the initiation phase is made so the process of execution may begin. The project plan serves as a roadmap for the entire process of project management.
Project planning involves:
- Defining Objectives The definition must include what the project is comprised of, its main aim, what it intends to accomplish, and what marks its closure
- Explaining the Scope The explanation provides details on what the project intends to solve and who will benefit from the project
- Scheduling Tasks Each task is given a start date, an end date, and provides an estimate of how much time a task would take to complete
- Generating Progress Reports The document includes the work to be performed, deliverables, and the intended outcome of the project
Project Planning Fundamentals
Project Planning refers to defining fundamentals such as the following:- Determination of Scope, Cost, and Resources: The process of determining the scope, cost, and resources help estimate the time required to complete the project, the number of people needed, and the skill set required.
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) helps this process by dividing the whole task into smaller, manageable segments
- Identification of the Problem: A variety of techniques, like surveys or meetings, are used to collect information to assess problems. There can be multiple problems; then, the project team selects the issue that requires the most immediate attention.
- Identification of Stakeholders: Identification of stakeholders gives a clearer image of the real problem, specifically which function or people might be affected by the project. Stakeholders work with the project team and contribute to the project's success
Definition of Project Objectives
A plan is made, keeping in mind the various expectations of the stakeholders
The success of the project entirely depends on how much of the expectations the project is able to meet
Project planning ensures timely testing of the output at every step. When successfully implemented, everyone on the project team can foresee problems before they happen. This creates efficiencies and ensures the successful execution of the plan.
Additionally, project planning helps analyze, prioritize, and ensure an appropriate plan for all kinds of risks. Proper planning ensures that if there is more than one risk, they can be prioritized and dealt with accordingly. This step ensures that nothing will fall apart and the plan makes it easy for the project team to remember all the crucial details and deadlines.
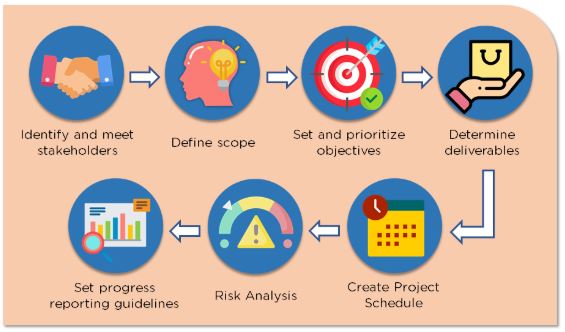
1. Identify and Meet Stakeholder
The stakeholders might include the project manager, the customer, or the team. The first step is to identify and meet the stakeholders to discuss their expectations and establish the project scope.
Why Project Planning?
Project planning ensures monitoring of the budget and schedule at every step. The project plan includes a schedule that guides team members in completing their tasks and helps them in knowing which tool they will need and when. It also helps the team stay engaged for higher project performance. The project plan ensures there is the active participation of all the team members and allows them to have an opportunistic approach towards their work.Project planning ensures timely testing of the output at every step. When successfully implemented, everyone on the project team can foresee problems before they happen. This creates efficiencies and ensures the successful execution of the plan.
Additionally, project planning helps analyze, prioritize, and ensure an appropriate plan for all kinds of risks. Proper planning ensures that if there is more than one risk, they can be prioritized and dealt with accordingly. This step ensures that nothing will fall apart and the plan makes it easy for the project team to remember all the crucial details and deadlines.
Project Planning Steps
There are seven essential project planning steps:The stakeholders might include the project manager, the customer, or the team. The first step is to identify and meet the stakeholders to discuss their expectations and establish the project scope.
2. Define Scope
Project scope involves determining a list of specific project goals, deliverables, budgets, and deadlines. Project scope helps in establishing boundaries of the project and responsibilities of each team member.
Project scope involves determining a list of specific project goals, deliverables, budgets, and deadlines. Project scope helps in establishing boundaries of the project and responsibilities of each team member.
3. Set and Prioritize Objectives
The objectives are set and prioritized once the expectations of stakeholders become certain. More exquisite detail to initial ideas is given, which serves as a reference point throughout the project.
The objectives are set and prioritized once the expectations of stakeholders become certain. More exquisite detail to initial ideas is given, which serves as a reference point throughout the project.
4. Determine Deliverables
Deliverables are the reason why the projects are created. It is one of the most critical steps of the project planning to determine what these deliverables will be and how they will be delivered in time.
Deliverables are the reason why the projects are created. It is one of the most critical steps of the project planning to determine what these deliverables will be and how they will be delivered in time.
5. Create a Project Schedule
The project schedule outlines when different tasks of a project are supposed to begin and end. The project schedule helps measure the project progress and set up progress reports.
The project schedule outlines when different tasks of a project are supposed to begin and end. The project schedule helps measure the project progress and set up progress reports.
6. Risk Analysis
Identifying risks and considering how to deal with them is an essential step in project planning. Specific steps to prevent risks from happening or limiting their impact should be considered.
Identifying risks and considering how to deal with them is an essential step in project planning. Specific steps to prevent risks from happening or limiting their impact should be considered.
7. Set Progress Guidelines
There must be a communication plan to update the stakeholders regarding the project progress. This can be done monthly, weekly, or daily so that all involved members can monitor the progress.
In conclusion, any project or endeavor that is not adequately planned is headed for failure from its very inception and it is our expectation that this piece would steer the reader in the direction of planning and following through on set plans to achieve successful and expected outputs.
culled from: https://www.simplilearn.com/tutorials/project-management-tutorial/project-planning
There must be a communication plan to update the stakeholders regarding the project progress. This can be done monthly, weekly, or daily so that all involved members can monitor the progress.
In conclusion, any project or endeavor that is not adequately planned is headed for failure from its very inception and it is our expectation that this piece would steer the reader in the direction of planning and following through on set plans to achieve successful and expected outputs.
culled from: https://www.simplilearn.com/tutorials/project-management-tutorial/project-planning
